Irritable Bowel Syndrome
Irritable Bowel Syndrome(IBS) is one of many bowel disorders that can cause anything from mild discomfort to extreme bowel issues. IBS belongs to a group of bowel disorders classified as non inflammatory bowel disorders as opposed to Inflammatory Bowel Disease which is characterized by inflammation of the intestines. So read further to understand what is IBS and how to manage the condition.
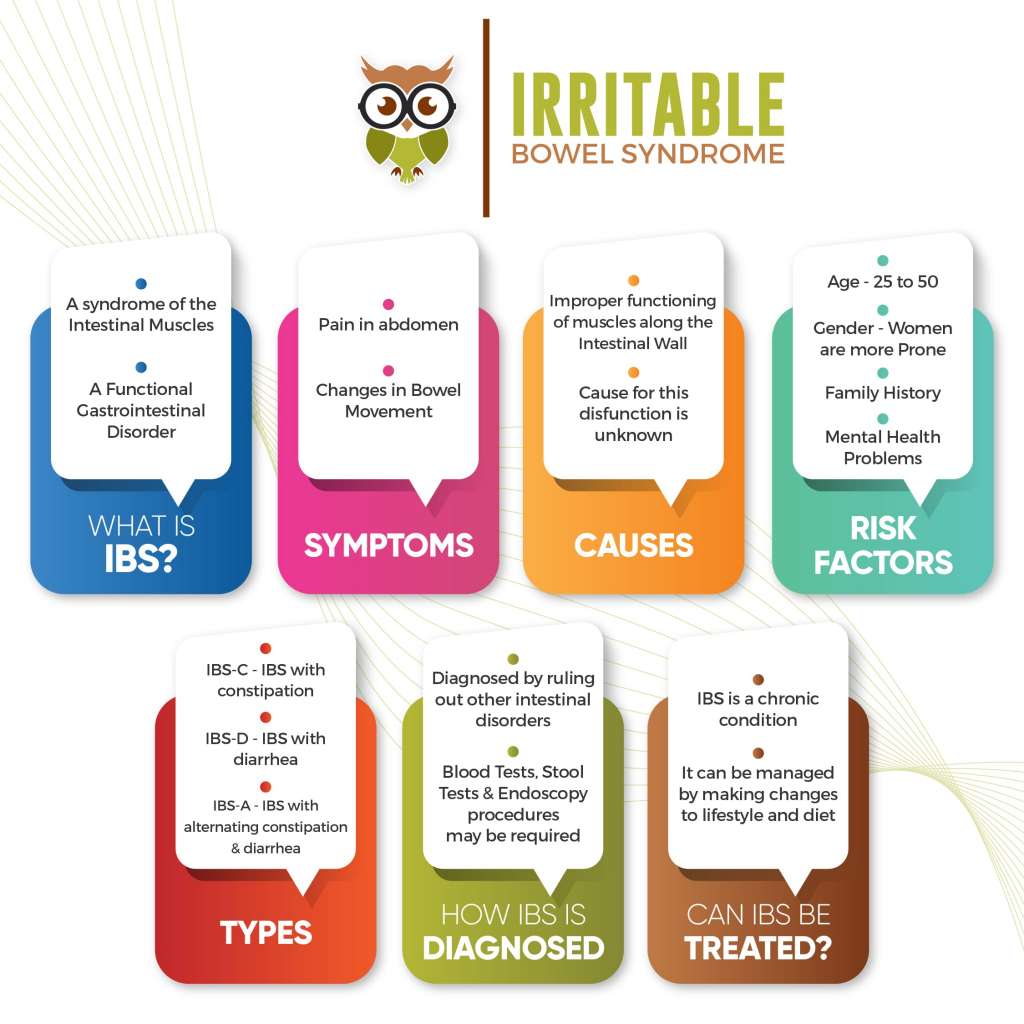
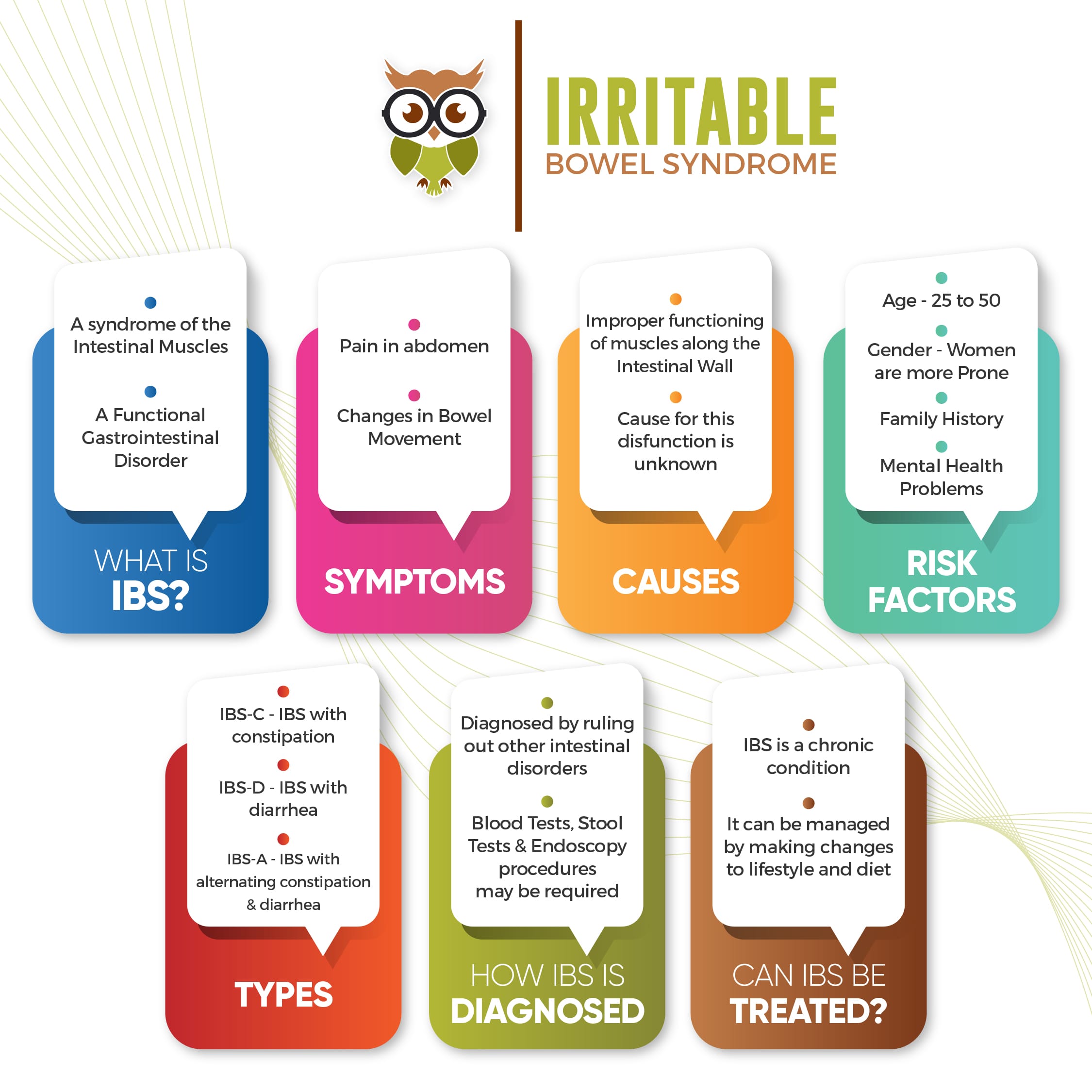
What Is Irritable Bowel Syndrome(IBS)?
IBS is classified as a functional gastrointestinal disorder where there are issues as to how the gut and brain work together. IBS is characterised by multiple symptoms such as stomach cramping, abdominal pain, bloating and changes in bowel movement. It is a chronic condition that tends to occur in people aged 20-45 and is seen more commonly in women.
What are the Symptoms of IBS?
IBS displays a varied range of symptoms. Some of the common symptoms are:
- pain in your abdomen (often related to your bowel movements)
- changes in your bowel movements (diarrhea, constipation, or in some cases, both)
A few of the other symptoms are:
- feeling bloated/gassy
- feeling very full
- mucous discharge in your stool
The symptoms of IBS tend to occur in episodes of symptom free periods followed by periods of severe burst of symptoms. Certain trigger foods might cause the onset of symptoms.
What are the causes of IBS?
The muscles lining the intestine play a vital role in pushing the food mass through the intestinal canal. As the food gets digested and water gets absorbed through the intestinal walls, undigested material forms the hard stool. In the case of IBS, the muscles tend to push the food through the canal too fast or too slow causing diarrhea or constipation respectively.
Although we are unable to pin-point what could cause this malfunction at this point of time, many theories have been put forth such as, oversensitive nerves in the intestine, intestinal muscle disorders,inflammations of the intestinal wall and genetics. Psychological stress and food intolerances are thought to be triggers as well.
What are the risk factors of IBS?
A few of the risk factors associated with IBS are as follows:
- Age – IBS tends to occur in people of the 25-50 age groups
- Gender – IBS seems to be more common in Women than Men. It is thought that the female hormones play a role in this
- Family History – Genes or a shared environment or both in combination may play a role in risk of IBS
- Mental Health Problems – Anxiety, depression and other mental health issues are associated with IBS
What are the types of IBS?
Based on the type of symptoms, IBS can be divided into 3 types namely:
- IBS-C – IBS with constipation characterised by Infrequent stools and constipation
- IBS-D – IBS with diarrhea characterised by frequent stools and diarrhea
- IBS-A – IBS with alternating constipation and diarrhea
Are IBS and IBD the same?
Although IBS and IBD share a lot of symptoms, they are completely different disorders. While IBS is characterised by multiple symptoms, it is not a disease in itself and is not considered to be as dangerous as IBD. IBD on the other hand causes inflammatory reactions and causes damage to the intestine leading to intestinal bleeding, rectal bleeding, ulcers, etc.,
A simple non-invasive test to differentiate between the two is to take a fecal calprotectin test which measures the presence of certain antibody proteins in the stool. A positive result indicates the presence of IBD while the negative test could mean that the symptoms may be caused due to IBS and needs further testing for confirmation.
How is IBS diagnosed?
After a review of your symptoms and their frequency, a doctor would recommend certain tests to diagnose IBS. This includes physical examination for bloating, tenderness or pain. IBS is mainly diagnosed by ruling out the presence of other disorders such as IBD and food intolerances(Gluten, Lactose, etc.,). The doctor might also recommend a routine blood and stool test and in some cases an upper GI endoscopy or a colonoscopy.
What is the low FODMAP diet?
FODMAP stands for fermentable oligo-, di-, and monosaccharides and polyols. It is a class of carbohydrates that are not well absorbed in the intestine for some people. This leads to food items getting accumulation in the intestine and fermented by the gut bacteria leading to release of gas.
These conditions tend to trigger IBS in individuals. The list of foods that are classified as FODMAPs is extensive and is maintained by the International Foundation for Functional Gastrointestinal Disorders and it is recommended to go on a low FODMAP diet and introduce one food at a time to identify the trigger food.
How does IBS affect quality of life?
Although there are very few complications associated with IBS, mental health and quality of life are the biggest complications individuals with IBS tend to face. Some people may feel they’ve lost control over their body as they can never be sure when they would have to go to the toilet.
Another issue is that it could be embarrassing to talk about issues with their bowel movements or passing a lot of wind often.
Can IBS be treated?
IBS is a chronic condition that does not have a complete treatment as of now. But the condition can be managed by changes in diet, lifestyle, certain medications and in some cases, mental health therapies. The process of finding what treatment works best is a trial and error process in order to identify certain trigger foods or conditions.
Based on the type of IBS, individuals may be prescribed with fiber supplements or laxatives to treat their condition.