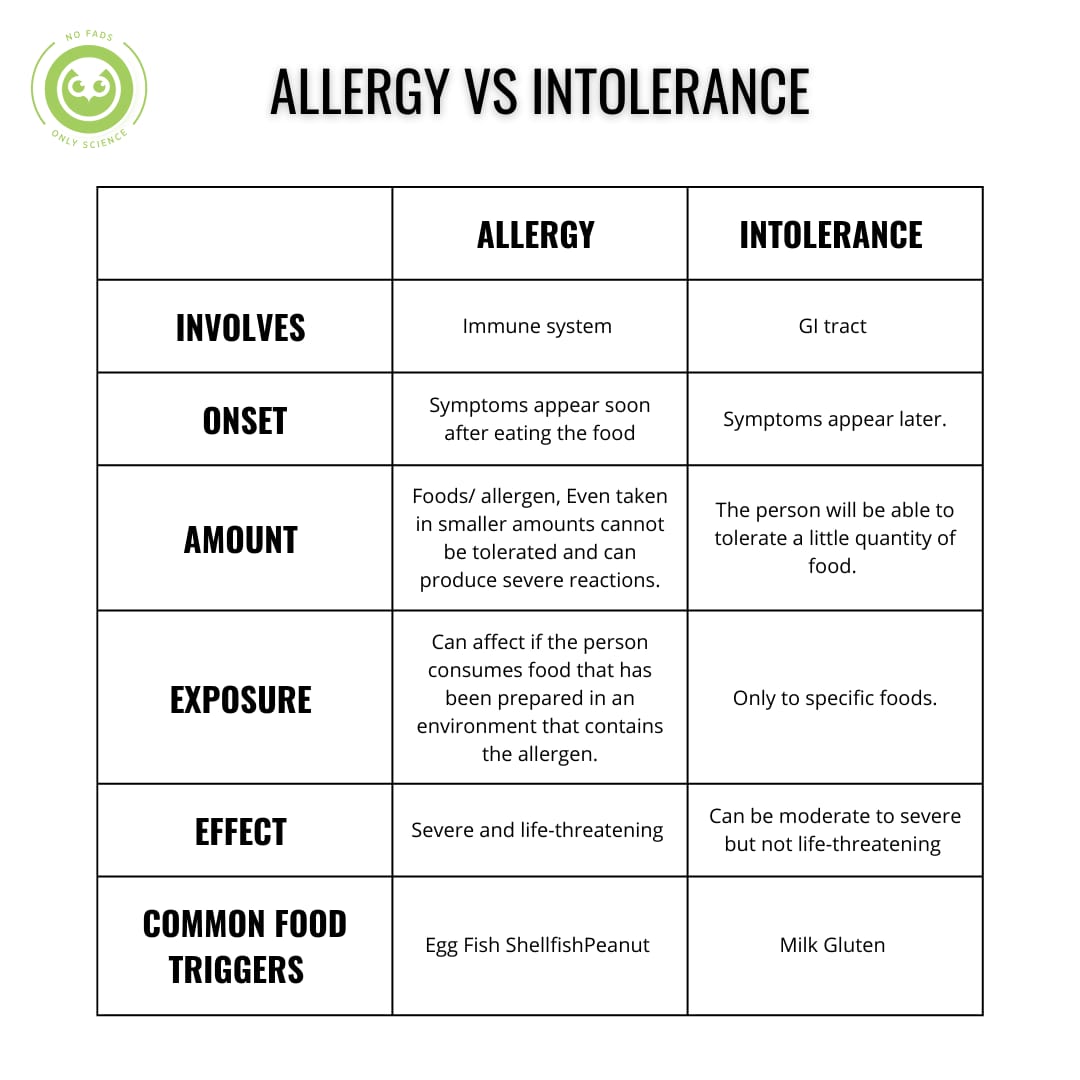
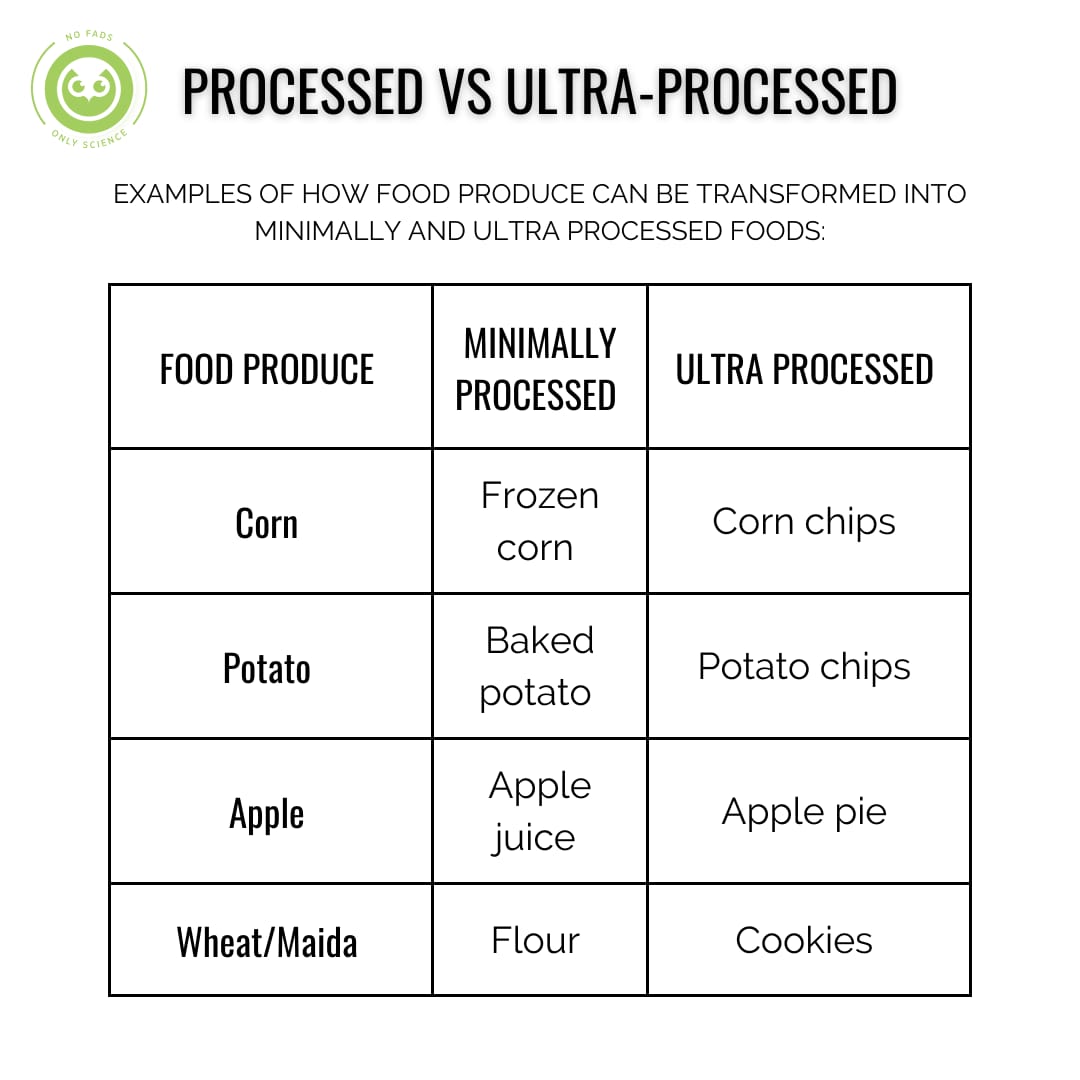
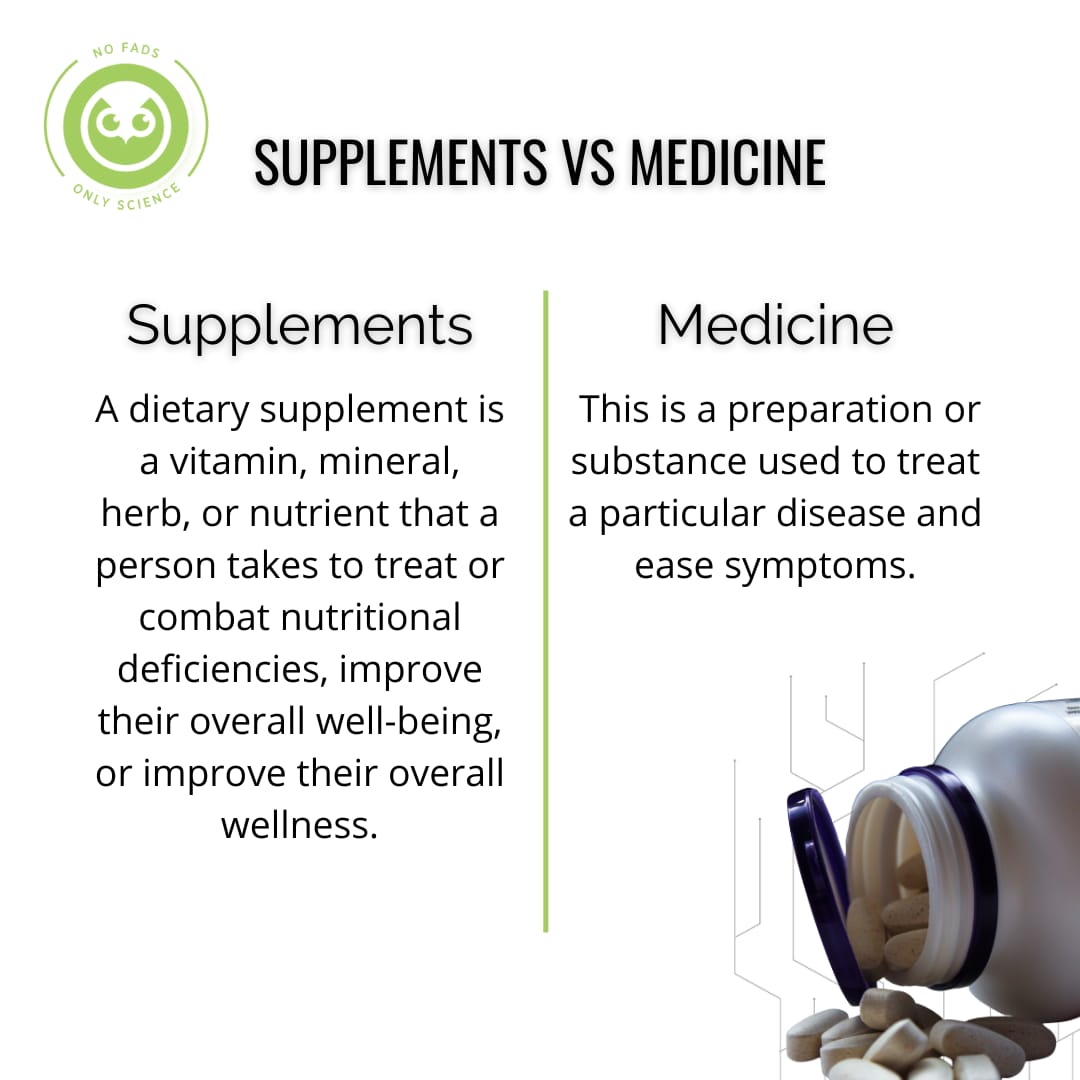
One of the most important determinants of fat loss is energy balance or the balance between the energy we consume through food and beverages and the energy we expend through physical activity and other bodily functions. When energy intake exceeds energy expenditure, the body stores the excess energy as fat, leading to weight gain. Conversely, when energy expenditure exceeds intake, the body must draw on its stored energy, resulting in fat loss.
Difference between fat loss vs weight loss:
Fat loss and weight loss may seem like interchangeable terms, but they are quite different.
So what’s the difference? Well, fat loss is more specific and targeted. When you lose fat you’re focusing on reducing the amount of adipose tissue, or fat in your body. This can improve your overall health and reduce the risk of chronic diseases such as type 2 diabetes and heart disease.
Weight loss on the other hand can be more general. When you lose weight, you could be losing fat, muscle, water, or even bone mass. While losing weight may result in some fat loss, it’s not the same thing as targeting fat loss specifically.
To lose fat, it is necessary to create an energy deficit by reducing energy intake or increasing energy expenditure, or ideally, doing both. Several strategies can help achieve this:
- Diet: Reducing energy intake through diet is one of the most effective ways to create an energy deficit and promote fat loss. This can be achieved by cutting back on calorie-dense, nutrient-poor foods such as processed snacks and sweets, and increasing the intake of nutrient-dense, low-calorie foods such as fruits, vegetables, and lean proteins. Research has shown that high-protein diets are particularly effective for fat loss, as protein can help preserve muscle mass and increase feelings of fullness, which can help with weight management.
- Physical activity: Increasing energy expenditure through physical activity is another key strategy for fat loss. Regular exercise has been shown to increase metabolic rate, reduce abdominal fat, and improve insulin sensitivity, all of which can help with weight management. In addition to its direct effects on fat loss, physical activity has numerous other health benefits, including improving cardiovascular fitness, mental health, and bone health.
- Lifestyle factors: Several lifestyle factors can impact energy balance and fat loss. Getting sufficient sleep, managing stress, and limiting alcohol intake can all help with weight management. Poor sleep and high levels of stress can disrupt hormone balance and increase the risk of weight gain, while excessive alcohol intake can contribute to weight gain by providing excess calories.
It is important to note that while creating an energy deficit is necessary for fat loss, the size of the deficit and the rate of weight loss can vary depending on individual circumstances. Factors such as age, gender, genetics, and starting weight can all impact the rate at which fat is lost. In general, it is recommended to aim for a weight loss of 0.5-2 lbs (0.2-0.9 kg) per week, as this is a safe and sustainable rate of loss that allows the body to adjust and minimize the risk of muscle loss.
Another important consideration when it comes to fat loss is the role of weight training. While aerobic exercises such as walking, jogging, and cycling can be effective for burning calories and promoting fat loss, weight training can also play a key role. Resistance training can help increase muscle mass, which can in turn increase metabolic rate and make it easier to maintain weight loss.
Myths about fat loss:
Myth 1: Low-fat diets are the best way to lose fat.
While it is true that creating a calorie deficit is important for fat loss, the type of calories consumed can also play a role. Low-fat diets, which are based on the idea that fat is the main cause of weight gain, have been popular for many years. However, there is little evidence to support their effectiveness for fat loss. Some research suggests that low-fat diets may be less effective than other types of diets, such as low-carb or high-protein diets, for weight loss.
Myth 2: Spot reduction is possible.
Spot reduction is the idea that it is possible to target specific areas of the body for fat loss, such as the belly or thighs, by doing exercises that specifically target those areas. However, this is not supported by scientific evidence. Fat loss occurs when the body uses stored fat as energy, and this process is largely controlled by hormones and genetics. It is not possible to selectively target specific areas of the body for fat loss.
Myth 3: Carbohydrates are bad for fat loss.
Carbohydrates have often been demonized as a cause of weight gain and poor health. However, this is not supported by scientific evidence. Carbohydrates are an important source of energy for the body, and they play several important roles in health. While it is true that reducing carbohydrate intake can be effective for weight loss, this is likely due to the calorie deficit that is created, rather than any specific effect of carbohydrates on fat loss.
Myth 4: Supplements and weight loss pills are effective for fat loss.
There are many supplements and weight loss pills on the market that claim to help with fat loss. However, the vast majority of these products have little to no scientific evidence to support their effectiveness. Some weight loss supplements can be dangerous and may even cause long-term health problems. The best way to lose fat is through a combination of diet and exercise, and there is no shortcut or quick fix.
Stress and fat loss:
When the body experiences stress, it activates the stress response, which involves the release of stress hormones such as cortisol. These hormones help the body cope with the perceived threat or challenge by increasing energy availability. This is achieved through several mechanisms, including the breakdown of stored glycogen and fat, and the suppression of non-essential processes such as digestion and immune function.
In the short term, this stress response can be beneficial, as it provides the body with the energy it needs to cope with the stressor. However, chronic or excessive stress can lead to an imbalance in energy metabolism, which can lead to weight gain or difficulty losing weight.
The relationship between stress and weight gain:
There is evidence to suggest that stress is associated with weight gain in several ways. One of how stress can lead to weight gain is by increasing appetite and food intake. Stress has been shown to increase levels of appetite-stimulating hormones such as ghrelin, and to reduce levels of appetite-suppressing hormones such as leptin. This can lead to an increase in food intake, particularly of high-fat, high-sugar, or comfort foods.
Stress can also lead to weight gain by disrupting the body’s ability to use energy effectively. Chronic stress has been shown to increase insulin resistance, which can lead to an increase in fat storage. Stress can also disrupt sleep, which can have negative effects on metabolism and energy balance.
Strategies for managing stress and promoting fat loss:
Given the negative effects of stress on energy balance and weight, it is important to find ways to manage stress to promote fat loss. Here are a few strategies that may be helpful:
- Practice mindful eating: When we are stressed, it can be easy to turn to food as a coping mechanism. However, this often leads to overeating or making unhealthy food choices. To counteract this, try to be more mindful when you eat. This means paying attention to your food and the sensations of hunger and fullness. Take the time to sit down and enjoy your meals, rather than eating on the go.
- Incorporate stress-reducing foods into your diet: Certain foods can help to reduce stress and improve overall well-being. These include foods high in omega-3 fatty acids, such as fatty fish, nuts, and seeds. Turmeric, a spice commonly used in Indian cuisine, has also been shown to have stress-reducing properties.
- Don’t skip meals: It can be tempting to skip meals when you are feeling overwhelmed, but this can increase stress and make it harder to lose fat. Instead, try to stick to a regular meal schedule and make sure to include balanced, nourishing meals.
- Stay hydrated: Dehydration can contribute to feelings of stress and fatigue. Make sure to drink plenty of water throughout the day to stay hydrated and reduce stress.
- Get enough sleep: Lack of sleep can increase stress and make it harder to lose fat. Aim for 7-9 hours of sleep per night to help manage stress and support fat loss.
- Incorporate physical activity: Exercise has been shown to reduce stress and improve overall well-being. Find an activity that you enjoy and aim for at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity exercise per week.
- Try stress-reducing techniques: In addition to diet and exercise, several stress-reducing techniques can be helpful, such as meditation, deep breathing, and yoga. Find what works best for you and try to incorporate these techniques into your daily routine.
Facts about fat loss:
- A calorie deficit is necessary for fat loss: To lose fat, you need to burn more calories than you consume. This can be achieved through diet and exercise, or a combination of both.
- Whole, unprocessed foods are generally more effective for fat loss: These types of foods tend to be more nutrient-dense and lower in calories, which can help with creating a calorie deficit.
- Protein is important for fat loss: Protein can help to increase satiety, or the feeling of fullness, which can make it easier to stick to a calorie deficit. In addition, protein has a high thermic effect, meaning that your body expends more energy digesting it compared to fat or carbs.
- High-fiber foods can be helpful for fat loss: Foods high in fiber tend to be more filling and can help to reduce hunger, which can make it easier to stick to a calorie deficit.
- Cutting calories too low can be counterproductive: While it is important to create a calorie deficit to lose fat, cutting calories too low can slow down your metabolism and make it harder to lose fat. It is important to find a balance and make sure you are still consuming enough nutrients to support your overall health.
- Regular exercise is important for fat loss: In addition to diet, regular exercise can help to increase calorie expenditure and promote fat loss. It is important to find physical activities that you enjoy and that are feasible for your lifestyle.
- Sustainable lifestyle changes are key for long-term fat loss: While it is possible to see significant changes in a short amount of time through crash dieting or extreme exercise, these changes are often not sustainable and can lead to weight regain. A slow and steady approach, with a focus on making sustainable lifestyle changes, is typically the most effective way to achieve long-term fat loss.
Sleep is very important for fat loss for several reasons, which are supported by evidence:
- Lack of sleep can lead to an increase in appetite: When we are sleep deprived, our bodies produce higher levels of the hormone ghrelin, which stimulates appetite. At the same time, levels of the hormone leptin, which suppresses appetite, decrease. This can lead to an increase in hunger and cravings for high-calorie, unhealthy foods.
- Lack of sleep can lead to an increase in calorie intake: Studies have shown that people who get less sleep tend to consume more calories than those who get enough sleep. This can make it harder to create a calorie deficit and lose fat.
- Lack of sleep can lead to a decrease in physical activity: When we are tired, we may be less motivated to exercise or engage in physical activity. This can lead to a decrease in calorie expenditure and make it harder to lose fat.
- Lack of sleep can lead to an increase in stress: Stress can lead to an increase in the production of the hormone cortisol, which can contribute to weight gain, particularly in the abdominal area. Getting enough sleep can help to reduce stress and prevent an increase in cortisol production.
- Lack of sleep can affect metabolism: Chronic sleep deprivation has been linked to impaired metabolism, which can make it harder to lose fat. Adequate sleep is important for maintaining a healthy metabolism and supporting fat loss.
In summary, getting enough sleep is important for fat loss for several reasons. It can help to reduce appetite and calorie intake, increase physical activity, reduce stress, and maintain a healthy metabolism. Aim for 7-9 hours of sleep per night to support fat loss.